An example of a low-mass boiler is a type of boiler that is characterized by its lightweight construction and rapid response to load changes. These boilers are commonly used in applications where quick steam generation and precise temperature control are required.
They offer several advantages, including compact size, high efficiency, and reduced emissions.
Low-mass boilers are designed with a smaller water content and a higher surface area-to-volume ratio compared to traditional boilers. This design enables faster heat transfer and reduces the time required to reach operating temperature. The compact size of low-mass boilers makes them suitable for space-constrained applications, such as in mobile units or small boiler rooms.
Low-Mass Boilers: Definition and Characteristics
Low-mass boilers are a type of boiler that is characterized by its low water content and fast response time. They are typically used in applications where rapid changes in heat demand are required, such as in space heating and process heating.
Low-mass boilers have several advantages over high-mass boilers, including their smaller size, lighter weight, and lower cost. However, they also have some disadvantages, such as their lower efficiency and higher maintenance requirements.
Advantages of Low-Mass Boilers
- Smaller size and lighter weight
- Lower cost
- Faster response time
- Easier to install and maintain
Disadvantages of Low-Mass Boilers
- Lower efficiency
- Higher maintenance requirements
- Shorter lifespan
Examples of Low-Mass Boilers: An Example Of A Low-mass Boiler Is A
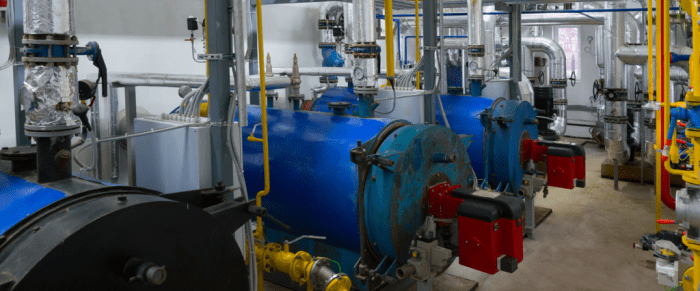
There are many different types of low-mass boilers available on the market. Some of the most common types include:
Fire-tube boilers
Fire-tube boilers are a type of low-mass boiler that is constructed with a series of tubes that are surrounded by water. The hot gases from the combustion process pass through the tubes, heating the water and creating steam.
Water-tube boilers
Water-tube boilers are a type of low-mass boiler that is constructed with a series of tubes that are filled with water. The hot gases from the combustion process pass over the tubes, heating the water and creating steam.
Condensing boilers
Condensing boilers are a type of low-mass boiler that is designed to recover the latent heat of vaporization from the flue gases. This makes them more efficient than other types of boilers.
Applications of Low-Mass Boilers
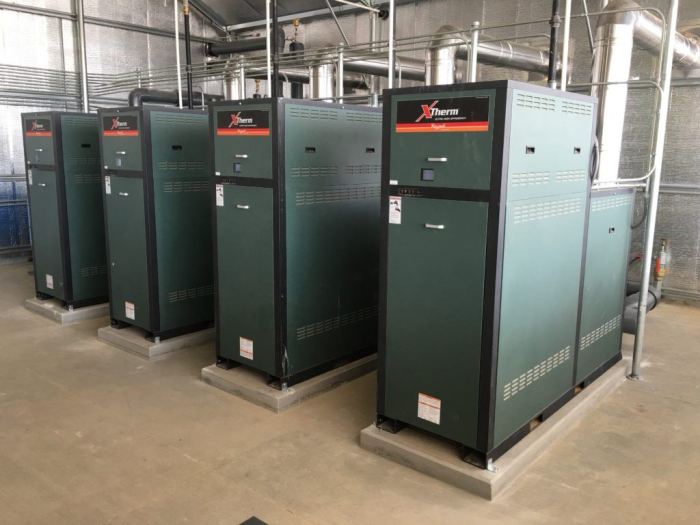

Low-mass boilers are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
Space heating
Low-mass boilers are often used to heat homes and other buildings. They are particularly well-suited for applications where rapid changes in heat demand are required, such as in homes with radiant floor heating systems.
Process heating
Low-mass boilers are also used in a variety of industrial and commercial applications, such as food processing, textile manufacturing, and papermaking. They are particularly well-suited for applications where precise temperature control is required.
Design Considerations for Low-Mass Boilers
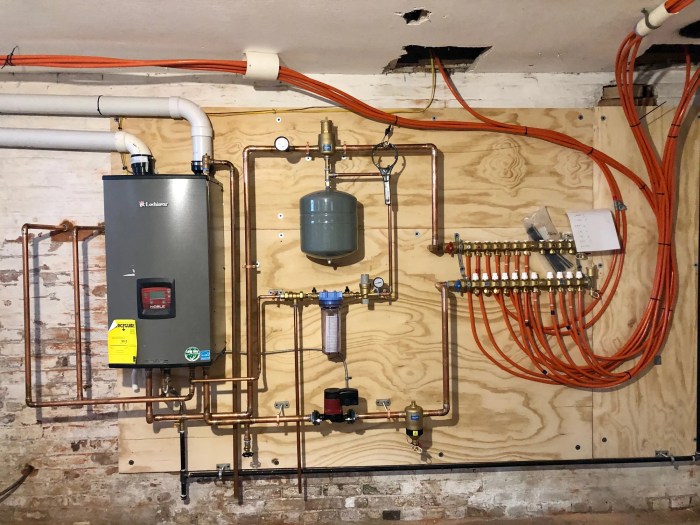
There are several important design considerations for low-mass boilers, including:
Materials
The materials used in the construction of a low-mass boiler must be able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures that are involved in the combustion process. Common materials used in the construction of low-mass boilers include steel, stainless steel, and copper.
Heat transfer, An example of a low-mass boiler is a
The design of a low-mass boiler must ensure that heat is transferred efficiently from the combustion gases to the water. This is typically achieved by using a combination of convection and radiation heat transfer.
Efficiency
The efficiency of a low-mass boiler is a measure of how much of the fuel energy is converted into heat. The efficiency of a low-mass boiler can be improved by using a variety of design features, such as a condensing heat exchanger.
Maintenance and Operation of Low-Mass Boilers
Low-mass boilers require regular maintenance to ensure that they operate safely and efficiently. Some of the most important maintenance tasks include:
Regular inspections
Low-mass boilers should be inspected regularly to check for any signs of damage or wear. These inspections should be performed by a qualified technician.
Cleaning
Low-mass boilers should be cleaned regularly to remove any soot or scale that may have accumulated on the heat transfer surfaces. This cleaning can be performed by a qualified technician or by the homeowner.
Water treatment
The water used in a low-mass boiler should be treated to prevent the formation of scale and corrosion. This treatment can be performed by a qualified technician or by the homeowner.
Comparisons with Other Boiler Types
Low-mass boilers are often compared to other types of boilers, such as high-mass boilers and condensing boilers.
Low-mass boilers vs. high-mass boilers
Low-mass boilers are smaller, lighter, and less expensive than high-mass boilers. However, they are also less efficient and have a shorter lifespan.
Low-mass boilers vs. condensing boilers
Low-mass boilers are more efficient than condensing boilers, but they are also more expensive. Condensing boilers are also more complex to install and maintain.
Questions Often Asked
What are the advantages of low-mass boilers?
Low-mass boilers offer several advantages, including compact size, high efficiency, reduced emissions, and rapid response to load changes.
What are some applications of low-mass boilers?
Low-mass boilers are commonly used in applications where quick steam generation and precise temperature control are required, such as in power plants, manufacturing facilities, and hospitals.
How do low-mass boilers differ from traditional boilers?
Low-mass boilers are designed with a smaller water content and a higher surface area-to-volume ratio compared to traditional boilers, resulting in faster heat transfer and reduced response time.