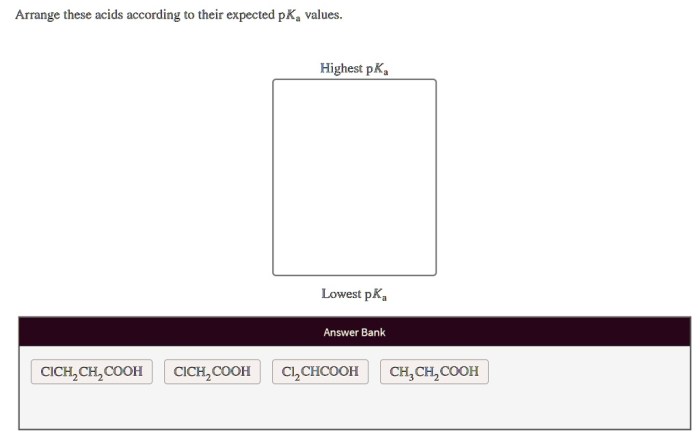
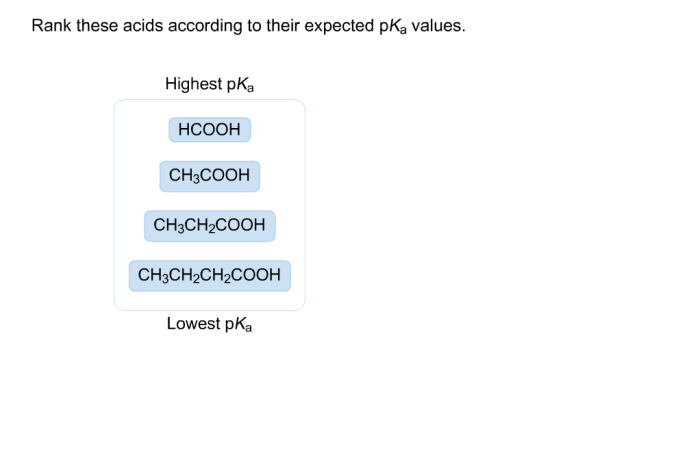
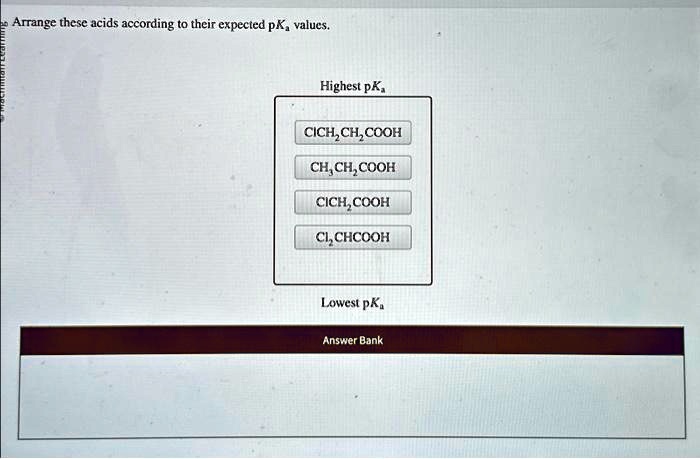
Arrange these acids according to their expected p𝐾a values. – Arrange these acids according to their expected pKa values: Understanding the pKa values of acids is crucial for comprehending their strength and behavior in chemical reactions. This guide delves into the factors influencing pKa values and provides a systematic approach to arranging acids based on their expected pKa values.
pKa values quantify the acidity of acids, indicating their tendency to donate protons. Acids with lower pKa values are stronger acids, while those with higher pKa values are weaker acids. This guide explores the relationship between pKa values and acid strength, providing insights into solution acidity and pH prediction.
Arranging Acids by pKa Values

The pKa value of an acid is a measure of its strength. A lower pKa value indicates a stronger acid, while a higher pKa value indicates a weaker acid. pKa values are important because they can be used to predict the behavior of acids in solution.
There are a number of factors that can influence the pKa value of an acid. These factors include:
- Electronegativity of the atoms bonded to the acidic hydrogen
- Resonance effects
- Inductive effects
- Solvent effects
In general, acids can be arranged according to their expected pKa values using the following criteria:
- Stronger acids have lower pKa values
- Weaker acids have higher pKa values
| Acid | Formula | pKa Value | Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrochloric acid | HCl | Strong | |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | Strong | |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 | Strong | |
| Acetic acid | CH3COOH | Weak | |
| Carbonic acid | H2CO3 | Weak |
The pKa value of an acid can be used to predict the pH of a solution. The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity. A lower pH value indicates a more acidic solution, while a higher pH value indicates a more basic solution.
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to calculate the pH of a solution:
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA])
where:
- pH is the pH of the solution
- pKa is the pKa value of the acid
- [A-] is the concentration of the conjugate base of the acid
- [HA] is the concentration of the acid
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation can be used to predict the pH of a solution of a known acid concentration.
FAQ Summary: Arrange These Acids According To Their Expected P𝐾a Values.
What is the significance of pKa values?
pKa values quantify the acidity of acids, indicating their strength and behavior in chemical reactions.
How do you arrange acids based on their pKa values?
Acids with lower pKa values are stronger acids, while those with higher pKa values are weaker acids.
What factors influence the pKa values of acids?
Electronegativity, resonance, inductive effects, and solvent effects all influence the pKa values of acids.